
Then, after a space (or tab), add the hostname. IP address) you want the hostname to point to. The syntax is fairly straight forward, first write the name of the host (e.g.
HOSTS FILE LOCATION HOW TO
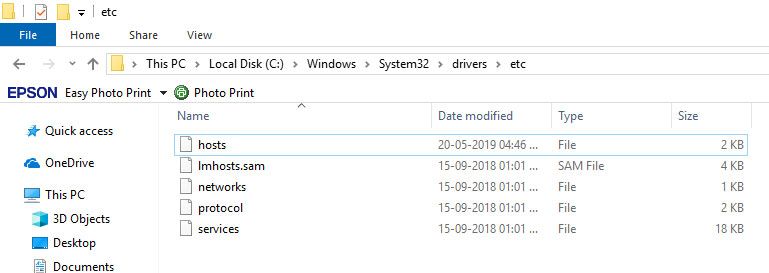
How to Edit the Hosts File on WindowsĮach hostname you want to define should be on one line (and there should be a new line for each hostname). Then, go to File > Open (or hit CTRL + O):įinally, paste the hosts file location from above into the File name: field and hit Open:Īnd that's you, inside the hosts file and ready to edit it! If you want to learn how to use the hosts file, read on. First, open Notepad as an administrator by right clicking it and selecting Run as Administrator: On Windows 8 and 10, you'll need to run the application you wish to open the hosts file with as administrator in order to access it. You can find it at the following path: C:\Windows\System32\Drivers\etc\hosts The hosts file location on Windows 10, Windows 8, and Windows 7 is the same. If you want to learn how to open up the hosts file, read on. A hosts file defines any and all hostnames that aren't in the domain name system, in fact, one can even override the DNS by changing the hosts file (as it has priority). It would also be possible to use the hosts file to declare these. In the case of and localhost, they both use system called DNS (domain name system) which - to really water things down - tells the computer where they point to. But how does your computer know which IP address a hostname points to? Perhaps the most-commonly used example of a hostname is localhost which is actually just a hostname for 127.0.0.1.

If we think about the IP address as the host, and the domain as the name, it's quite clear to see where the name "hostname" comes from: it's the name for a host. When you visit a website, for example Save Location, the domain (in this case, ) is just an alias for an IP address.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
